Outdated documentation
You are reading outdated documentation. This page documents ChirpStack v3. ChirpStack v4 is the latest version.
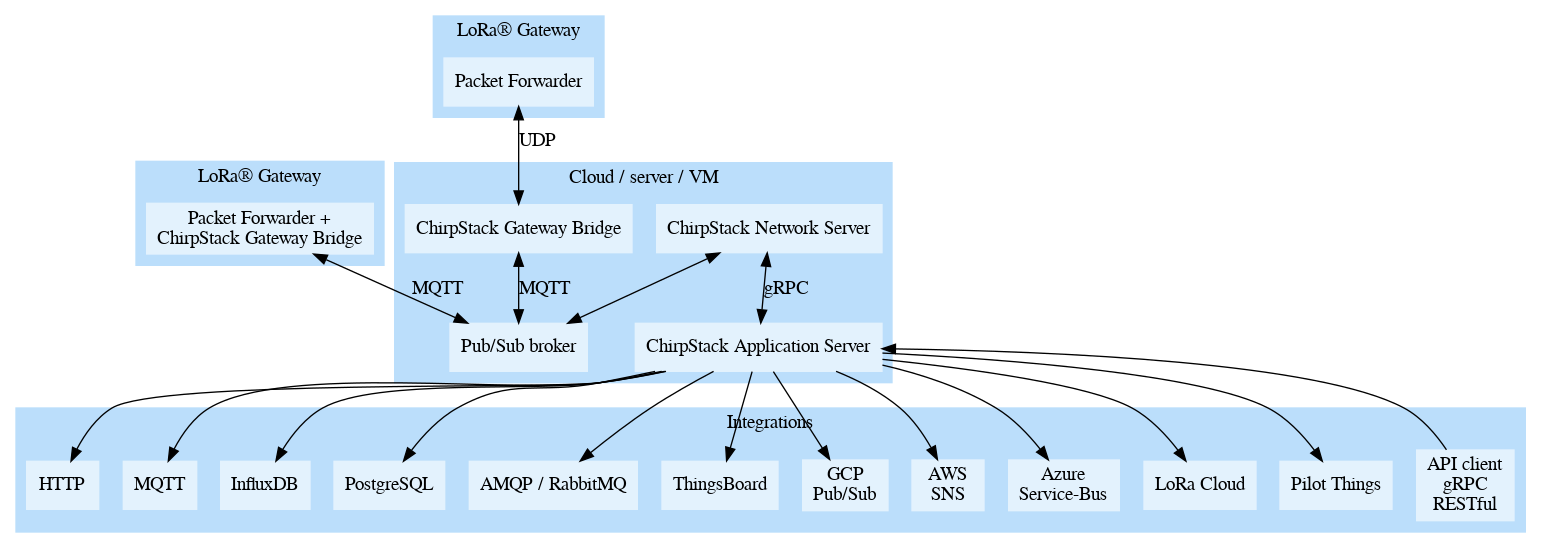
ChirpStack architecture
The graph below visualizes how the ChirpStack LoRaWAN® Network Server components are connected:
LoRaWAN devices
The LoRaWAN devices (not pictured in the above graph) are the devices sending data to the ChirpStack Network Server (through one or multiple LoRa Gateways). These devices could be for example sensors measuring air quality, temperature, humidity, location...
LoRa® Gateway
A LoRa Gateway listens to (usually) 8 or more channels simultaneously and forwards received data (from devices) to a LoRaWAN network-server (in this case the ChirpStack Network Server). The software running on the LoRa Gateway responsible for receiving and sending is called a Packet Forwarder. Common implementations are the Semtech UDP Packet Forwarder and the Semtech Basic Station Packet Forwarder.
ChirpStack Gateway Bridge
The ChirpStack Gateway Bridge sits between the Packet Forwarder and MQTT broker. It transforms the Packet Forwarder format (like the Semtech UDP Packet Forwarder protocol) into a data-format used by the ChirpStack components. It also provides integrations with various cloud platforms like GCP Cloud IoT Core and Azure IoT Hub.
ChirpStack Network Server
The ChirpStack Network Server is a LoRaWAN Network Server, responsible for managing the state of the network. It has knowledge of device activations on the network and is able to handle join-requests when devices want to join the network.
When data is received by multiple gateways, the ChirpStack Network Server will de-duplicate this data and forward it as one payload to the ChirpStack Application Server. When an application-server needs to send data back to a device, the ChirpStack Network Server will keep these items in queue, until it is able to send to one of the gateways.
ChirpStack Application Server
The ChirpStack Application Server is a LoRaWAN Application Server, compatible with the ChirpStack Network Server. It provides a web-interface and APIs for management of users, organizations, applications, gateways and devices.
Received uplink data is forwarded to one or multiple configured integrations.
End-application
The end-application receives the device-data through one of the configured integrations. It can use the ChirpStack Application Server API in order to schedule a downlink payload to the devices. The purpose of an end-application could be analytics, alerting, data visualization, triggering actions, ...